Content table
Feeling a bit overwhelmed by your upcoming hCG trigger shot?
Or just want to ensure that you know exactly what to expect? We’re here to fill you in on all the dos and don’ts of trigger shots.
The “trigger shot” is used for stimulating ovulation in IUI, IVF, and timed intercourse cycles. And if you avoid making common hCG trigger shot mistakes, it can greatly improve your chances of conceiving.
One study found two impressive findings with the hCG trigger shot. First, when the trigger shot was used before intrauterine insemination, pregnancy rates increased by 12.4%. When used with the natural timing of the LH surge, the pregnancy rate increased by nearly 31%.
Clearly, the hCG trigger shot is a powerful aspect of many fertility treatments. So keep reading for an overview of how it works and learn common mistakes you should avoid.
Key Takeaways
- Keep in mind that the hCG trigger shot is one step in a larger fertility treatment plan.
- In IVF, you’ll do the trigger shot before your egg retrieval procedure. In IUI, the trigger is given before the insemination. That’s why the timing of the shot is so important.
- Administer the trigger shot according to your doctor’s directions and the manufacturer’s instructions. This will give you the best chance of successful conception and ensure your safety.
- Talk to your fertility specialist about any additional questions or concerns you may have. And consider opening up to a trusted friend or fertility warrior for moral support for this leg of your fertility journey.
How Does the hCG Trigger Shot Work?
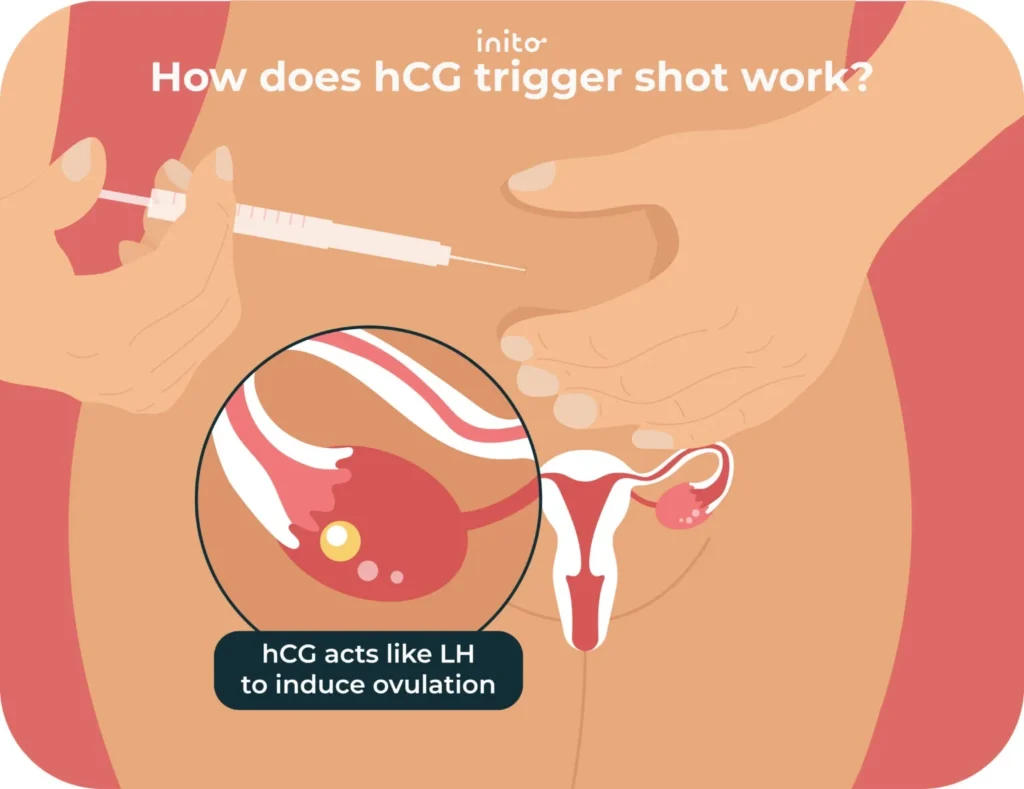
hCG trigger shots set off ovulation by taking the role of Luteinizing Hormone (LH). It is for women undergoing ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology) who do not have optimal ovulatory function or LH patterns.
An hCG trigger shot is a synthetic version of human chorionic gonadotropin. Common drug names for the hCG trigger are Pregnyl®, Ovidrel®, Profasi®, and Noravel®.
These medications are prescribed as part of an assisted reproduction plan. Unlike in the natural menstrual cycle, where the LH surge helps eggs reach maturity, in ART, hCG trigger shots help with the maturation and release of the egg(s).
In short, hCG trigger shots take on the role of LH by releasing the eggs from the ovary, starting ovulation.
Now, how does the hCG trigger shot induce ovulation?
hCG and LH actually have a lot in common:
- The molecular structure of hCG and LH is very similar.
- They both share the LH/CGR receptor.
- They share the same alpha subunits.
- Both have a similar amount of cysteine (an amino acid).
Their natural purpose is also the same: To assist lutein cells and induce ovulation.
In short, LH and hCG are similar and can bind to the same receptors. This allows hCG to act as LH and induce ovulation.
Now that you’ve seen exactly how the trigger shot works, let’s go over some mistakes you should avoid.
See how your hormone chart might look like!
Answer some questions to help us provide you a free personalized hormone chart customized to your hormonal health and conditions
Common hCG Trigger Shot Mistakes (And How You Can Avoid Them)
Look at the chart below to learn about common mistakes women sometimes make with the hCG trigger shot.
And more importantly, read the right-hand side to learn what you can do to make sure you don’t make these mistakes yourself!
hCG Trigger Shot Mistake | How to Avoid? |
Incorrect timing | Use the medication exactly when your fertility specialist asks you to. |
Improper storage | Store the medicine as directed by the manufacturer.
|
Improper administration (from either the dosage or the injection technique) | Carefully follow the instructions of the manufacturer and your fertility doctor. |
Not rotating the injection site (if administering more than one shot) | Change the site of the injection for subsequent administrations. |
Not confirming ovulation (in timed natural cycles) | Confirm that ovulation occurred. You can check PdG and progesterone levels or get an ultrasound. |
Failure to report side effects | Watch for any unusual reactions or side effects. If you notice anything abnormal, call your doctor right away. |
Let’s get an even better understanding of each of these six mistakes. That way, you’ll have a full picture of the proper hCG trigger shot protocol.
1. Incorrect timing
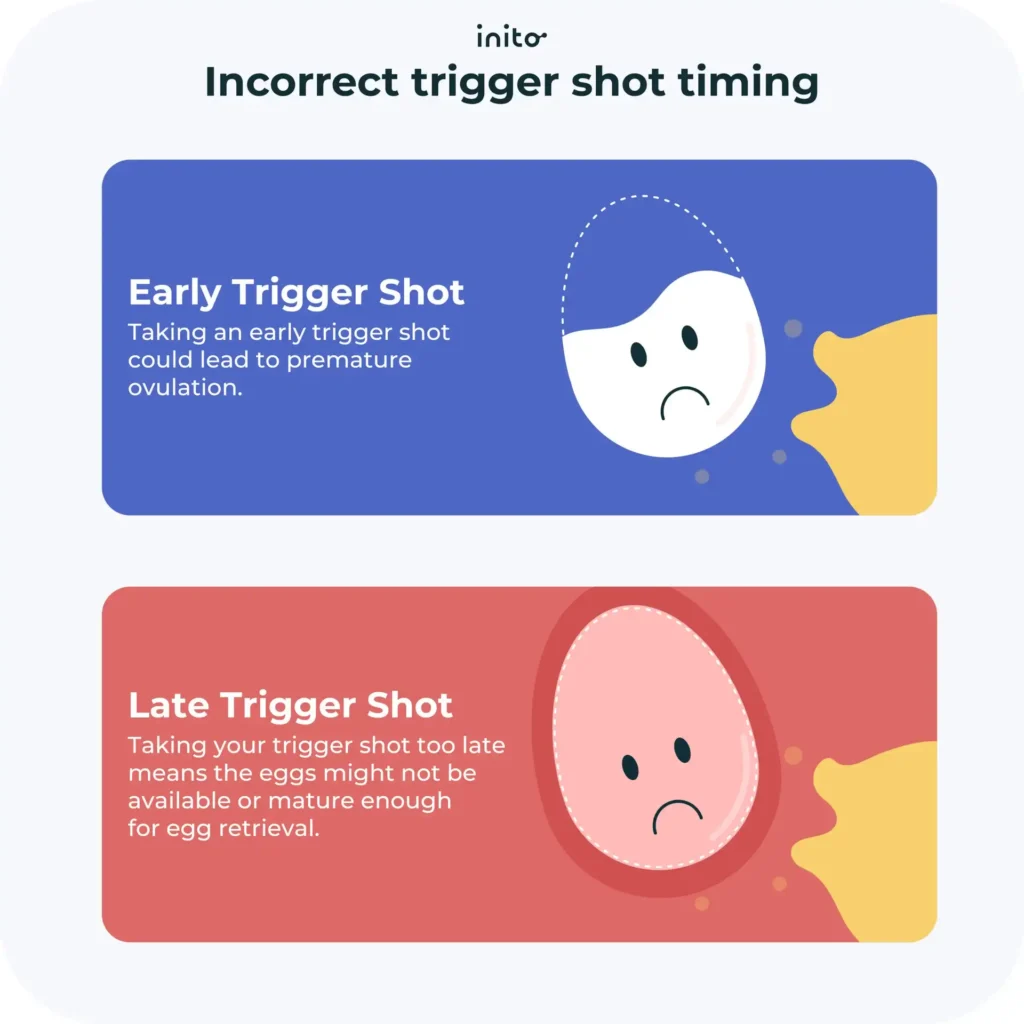
Administering the trigger shot at the right time is very important. This is because the hCG shot is just one part of a larger sequence of events in your fertility treatment. And throwing off the precise timing of the trigger shot could impact the timing of follow-up procedures.
For example, one trial found that performing an IUI 42 hours (instead of 36 hours) after the trigger shot led to significantly higher pregnancy rates. Just four hours made a difference in success rates.
What happens if a trigger shot is too early?
Typically, you can expect to ovulate about 36 hours after administering the shot. So if you take the trigger shot too early, you could have premature ovulation. Whether you’re doing an egg retrieval procedure or insemination, this would throw off the timing for the next step of your fertility treatment.
What happens if you take a trigger shot too late?
Taking the trigger shot too late could hurt your chances of conceiving in that cycle. This is because if the trigger is taken too late, the eggs may not be available or mature enough at the time of egg retrieval. So the egg retrieval procedure would need to be rescheduled to a later date or time.
The bottom line with timing your trigger shot?
Follow your doctor’s instructions wholeheartedly. They know the entire timeline of your fertility plan. Do your part by administering the shot when you’re directed to. And of course, if you encounter any challenges with the timing, reach out to your HCP right away.
2. Improper storage
Like all medications, your trigger shot will come with precise storage directions from the manufacturer. If you don’t follow these directions for storage, the drug could end up being ineffective. So make sure to read all of the instructions carefully before the injection.
To give you a heads-up, the directions for your trigger shot probably look something like this:
For liquid injections (Ovidrel® comes in a pre-filled syringe)
- Store the medication in the fridge as soon as you get it.
- When you’re ready to use it, warm it with your hands before administering the injection.
- If used within 30 days, the medication can be safely stored at room temperature which is 68–77°F (20–25°C).
For powder forms (Pregnyl®, Profasi®, and Novarel®)
- Store the unmixed hCG and diluent (sterile water) at room temperature.
- Keep the medication away from any moisture or heat.
- After mixing the powder with the sterile water, you may store it in the fridge.
Disclaimer: The guidance above is meant to provide you with a general idea of basic storage best practices for hCG trigger shots. But you should follow the exact directions that came with your prescribed medication.
3. Improper administration dosage or technique
Administering the hCG trigger shot exactly as directed by your HCP is vital for treatment success. It’s also important for avoiding potential adverse reactions.
Here’s an overview of what to expect for hCG trigger shot dosage and administration.
Proper dosing:
- Your exact dosage will vary depending on your specific fertility treatment plan. Use the exact dosing directions provided by your doctor.
- If using the pre-filled syringe, the dosing is usually 250 mcg.
- If using the powder, the dosing is usually 5,000, 10,000, or 20,000 units.
Proper administration:
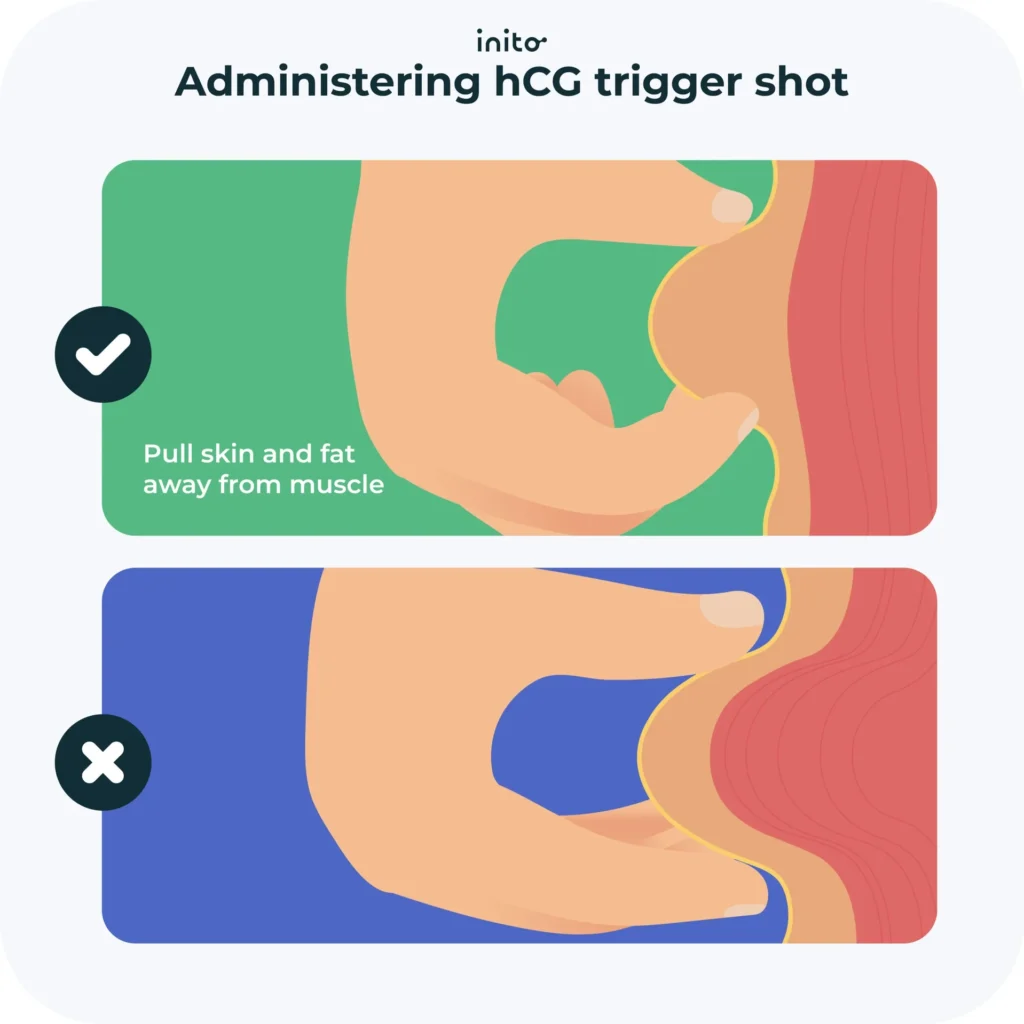
- You will likely be directed to administer the trigger shot on your own at home.
- If you’re unable to self-inject, you may be able to go to the doctor’s office or have someone else help you. Talk to your doctor about your options if you can’t do it yourself.
- This medication is most commonly injected either intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Let’s examine each of these more closely.
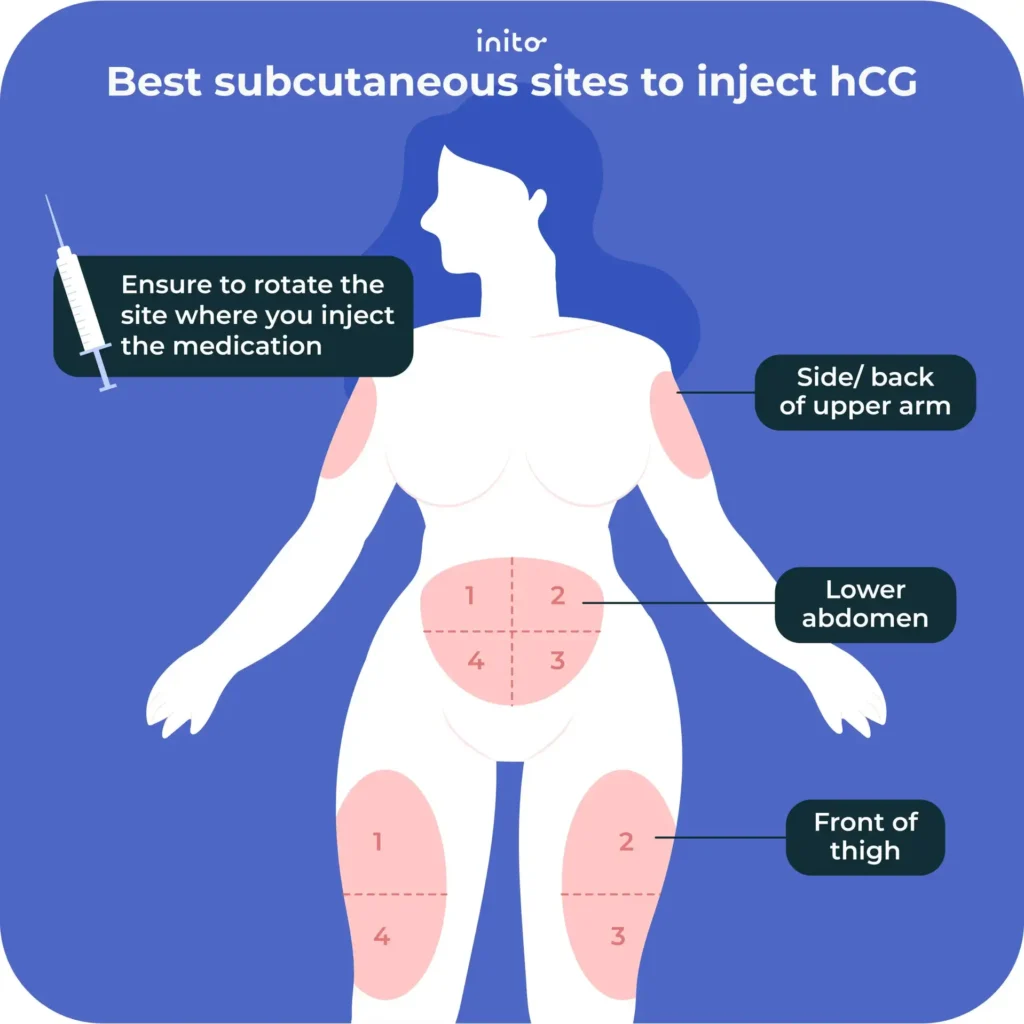
- Subcutaneously (SC): You will inject the needle just below the surface of your skin. The best places to inject via SC are the front of the thigh, your lower abdomen or the front or back of your upper arm.
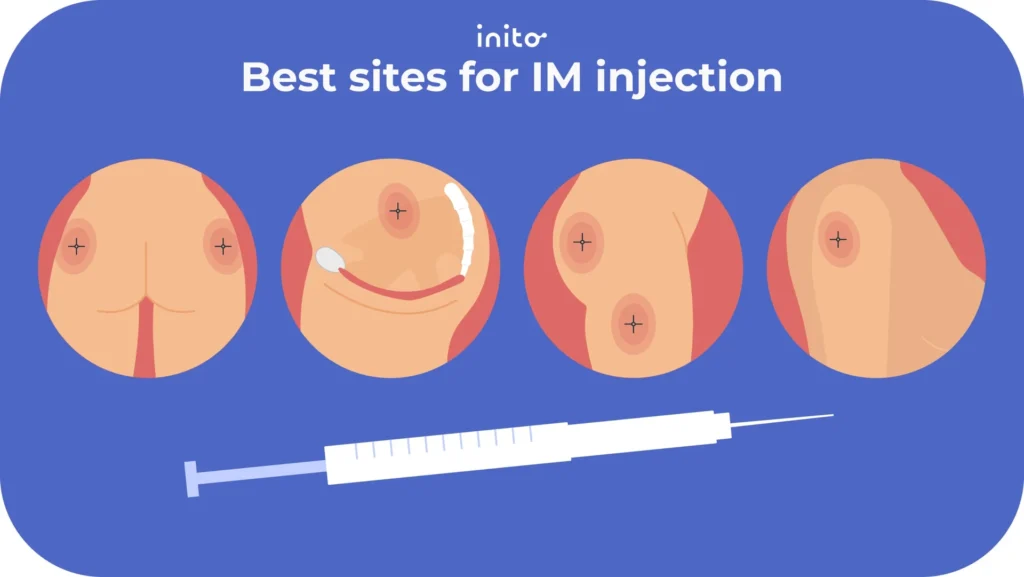
- Intramuscularly (IM): You will inject the needle into the muscle. The injection site can be around your upper thigh or lower abdomen.
4. Not rotating the injection site
- If you’re taking daily shots of gonadotropins, be sure to rotate the site where you inject the medication.
- Administering multiple injections in the same area may cause pain, irritation, or inflammation at the injection site.
- There are several acceptable injection sites, whether you’re injecting via IM or SC. Take a look at the images below to see the proper injection sites for each type of injection.
- Best sites for IM injection –
5. Not confirming that you ovulated after the injection
- For women using the trigger shot in a natural timed intercourse cycle, it’s important to confirm ovulation.
- You can do this by getting a blood test or ultrasound at your doctor’s office.
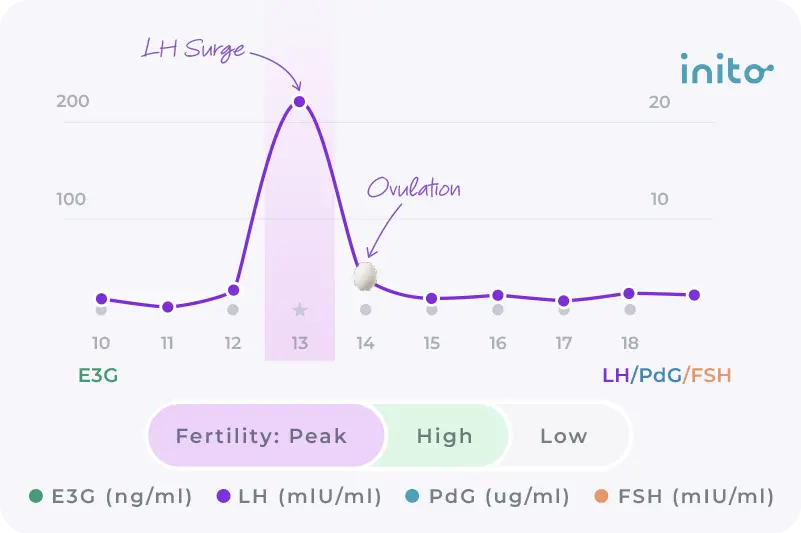
You can also confirm ovulation at home using the Inito fertility monitor , which measures your urine PdG levels. (PdG is the urine metabolite of progesterone and it rises when you ovulate.)
- In rare cases, the hCG shot may not be absorbed properly into your system. This could impact when you ovulate (if you even ovulate at all). But this is unlikely to happen if you use the medication as directed.
6. Not reporting side effects
Be on the lookout for any side effects after injecting the medication.
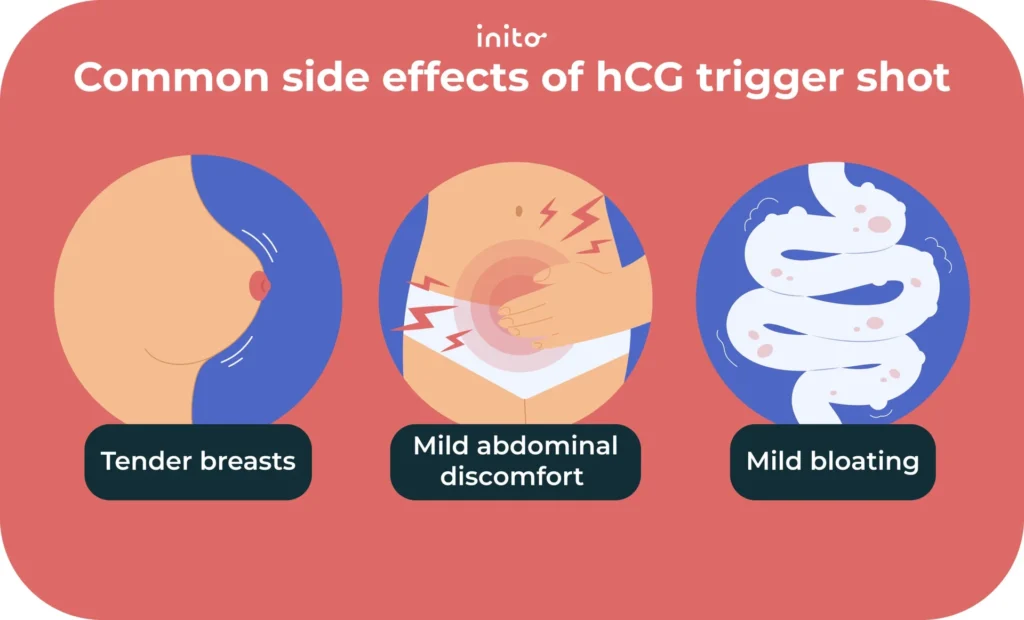
Be on the lookout for any hCG trigger shots side effects. Here are a few common ones:
- Tender breasts
- Mild abdominal discomfort
- Mild bloating
But if you experience any of these symptoms below, call your doctor ASAP:
- Excessive swelling
- Severe pain
Any other symptoms that are unusual or concerning
One more side effect to be aware of is called Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) – an exaggerated response due to the excess hormones. In general, OHSS is mild.
But in some cases, it could present with the following symptoms like:
- Severe pelvic pain
- Swelling of the hands or legs
- Stomach pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden weight gain
- Diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Decreased urination
If you experience any severe symptoms or signs of OHSS, seek medical attention immediately.
When Should You Go to the Doctor?
After administering the shot, call your doctor ASAP if you…
- Notice any severe side effects
- Mistimed the dose
- Accidentally took an extra dose
How Else Can You Prepare for the hCG Trigger Shot?
Still feeling a bit nervous about the hCG shot?
Do these 3 things to prepare yourself better:
- Carefully read any directions or watch any videos provided by your fertility specialist. Do this well in advance of administration. Having a clear idea of exactly what you’re expected to do can help reduce any additional anxiety before injecting the medication.
- Ask your doctor about anything you’re still confused about. Don’t worry about feeling “pesty.” If there’s an aspect of administering the shot that you don’t understand, it’s better to ask. This will help you avoid unintended errors. So ask (and ask again). But avoid holding on to any lingering concerns.
- Talk to other women for support. Though it may feel like it at times, you’re not in this alone. The hCG injection is a common step in many fertility treatments. Opening up to other women and listening to their experiences and advice may help you feel more prepared.
Join Inito’s Facebook group. This group is a supportive community of women navigating their fertility journey.

FAQs
As long as you follow the directions provided by your doctor and the drug manufacturer, the trigger shot should work as expected. It is possible that the medication doesn’t absorb properly. But this is very rare.
Don’t panic or take a second dose if you messed up your first attempt! If you have followed the correct technique, have peace of mind that the trigger shot will do its job. If for some reason you think something went wrong, call your doctor for guidance on what to do next.
The most reliable sign that the trigger shot worked is confirmed ovulation. The Inito monitor can help you test PdG levels in your urine to confirm ovulation. You can also get a blood test or ultrasound at your doctor’s office.
Remember, you should expect to ovulate about 36 hours after taking the hCG trigger shot. Noticing mild symptoms like bloating or breast tenderness can also indicate that the hCG was properly absorbed.
Was this article helpful?
- Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation with Intrauterine Insemination Is More Successful After r-hCG Administration Than Spontaneous LH Surge – PMC
- Effect of HCG-Triggered Ovulation on Pregnancy Outcomes in Intrauterine Insemination
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin: The Pregnancy Hormone and More – PMC
- Comparing the Effectiveness of Doing Intra-uterine Insemination 36 and 42 Hours After Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Injection on Pregnancy Rate: A Randomized Clinical Trial – PMC
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) injectable Uses, Side Effects & Warnings