Content table
Struggling to conceive naturally? Or need to use donor sperm? IUI and other forms of artificial reproductive technology (ART) could be an option for you.
Nowadays, nearly 2.3% of babies born in the U.S. are conceived using ART. The IUI procedure is one of these methods that can help with getting pregnant.
Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about what an IUI is, who it helps, success rates, and more.
What is IUI?
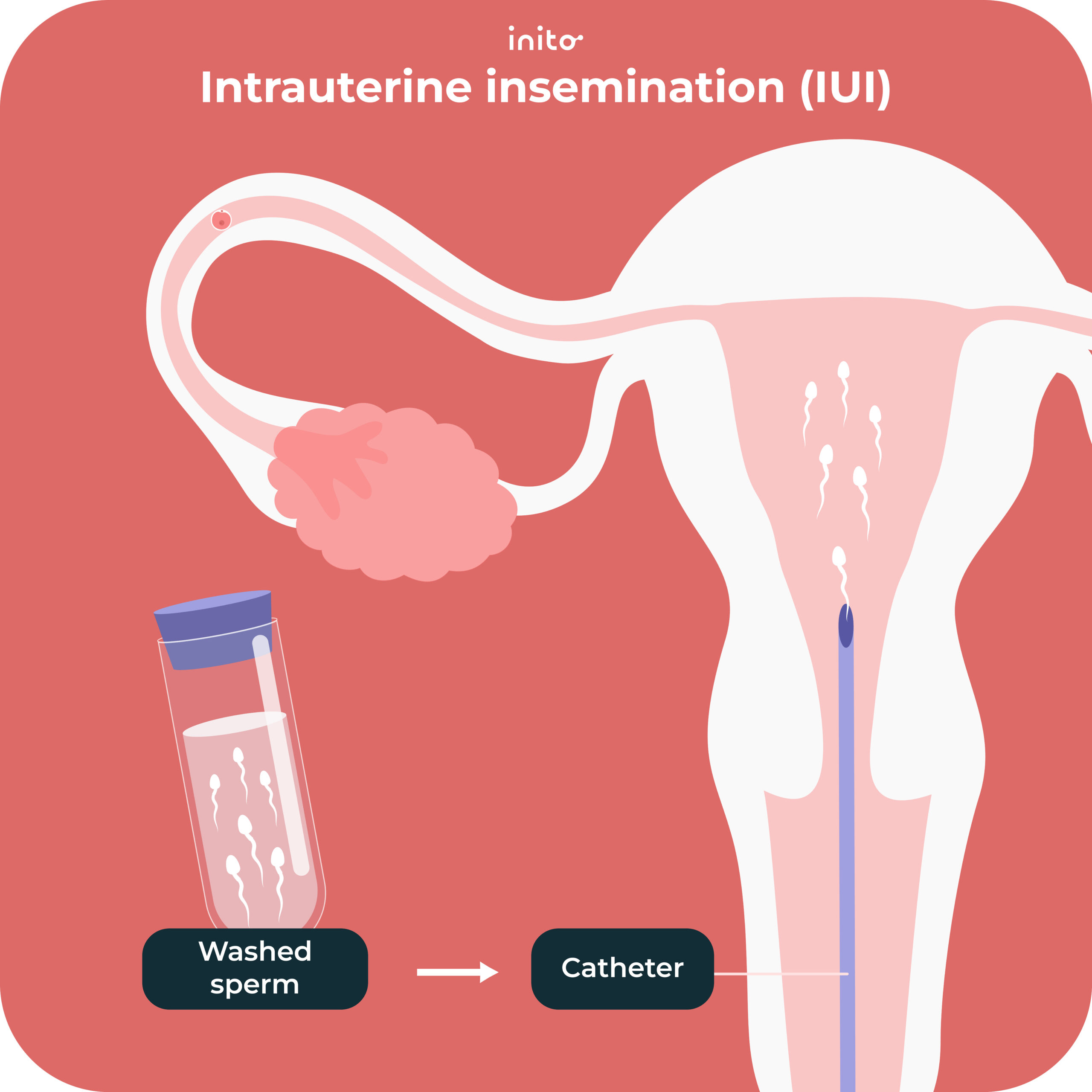
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a procedure where sperm is placed inside the uterus. This puts sperm closer to the fallopian tubes where it can meet up with an egg soon after ovulation.
In a natural cycle, sperm has to bypass the vagina and cervix. (Both of these are harsh environments for sperm to survive). By skipping past these, IUI helps increase the chances of fertilization and pregnancy.
Know more: How To Confirm Whether Sperm Went Inside?
Think of it this way:
Imagine IUI is a friend trying to set two individuals up on a date at the local mall. Without IUI’s help, the individuals show up to the same mall but still have to find their way to each other. With IUI’s help though, they’re directed to the same store right from the start.
Now that you get what IUI is, let’s tackle the question: how is IUI done?
What is the IUI procedure?
Believe it or not, much of the IUI process mirrors the same steps as natural conception. The main difference is the preparation and controlled placement of the sperm.
When you undergo an IUI, the sperm is “prepared,” meaning it’s washed and inspected for quality. Then around 24 to 36 hours before ovulation, the washed sperm is inseminated into the uterus.
From there, it’s still up to the sperm to fertilize the egg just like in a natural cycle. And then the fertilized egg must implant into the uterine lining. This is when a pregnancy becomes official!
That’s the gist of the IUI process. But depending on your unique fertility needs, there may be additional steps involved.
These extra steps could include: extra monitoring, ovulation induction, and the hCG trigger shot. Want an even more zoomed-in look at each step? Keep reading!
What are the steps of an IUI?
1. Consultation and testing
Before an IUI, your fertility specialist will first review your medical history. They may also run various diagnostic tests to determine if IUI is a fitting treatment option for you. This could include blood work as well as a transvaginal ultrasound.
During this phase, the doctor will also begin to predict your ovulation window. Knowing that information will help with an estimated timeline for your intrauterine insemination.
Heads up! This initial testing phase could take one cycle or several cycles. It all depends on your unique medical circumstances and how much testing is needed.
2. Ovulation induction
This is one of the major decisions that you’ll need to make when undergoing IUI. You can proceed with a natural cycle (unmedicated) or with ovulation induction (medicated).
IUI with a natural cycle
- Ovarian follicle growth and ovulation occur naturally with no medical intervention.
- The IUI is simply needed to get the sperm to the right place at the right time.
- This is typically the route taken for single women, lesbian couples, or females with no known fertility issues.
IUI with a medicated cycle
- Medication is taken to help mature multiple eggs (instead of only one). This can increase the chances of successful ovulation.
- Medicated IUI cycles are usually used in cases of minor female infertility and in some cases of unexplained infertility.
- Common ovulation induction medications include clomiphene citrate (CC), letrozole, and gonadotropins. As with any drug, each of these medications has its pros and cons (more on these below).
Here’s a glimpse into what research shows about IUI with these medications.
One study found that live birth rates were generally the same regardless of which medication was used to stimulate ovulation. There was one key difference that did surface though. Rates of conceiving multiples were the highest when clomiphene citrate was taken.
Another study showed a link between letrozole and a reduced likelihood of multiples. (This was in comparison to gonadotropin and CC cycles). It’s definitely worth thinking through all of this if you decide to do a medicated IUI cycle.
Know more: Clomid® vs. Letrozole: A Complete Comparison
3. Ovulation (egg release)
Another key decision in IUI involves the timing of ovulation.
Here are the two options:
- Allow the mature egg to be released naturally
- Use an hCG trigger shot (ovulation is expected 36 hours after the trigger shot)
Know more: Six Common hCG Trigger Shot Mistakes to Avoid
Before this decision is made, your fertility specialist will monitor your follicle growth. This is done through a transvaginal ultrasound at the doctor’s office or by tracking your LH surge at home.
The ultrasound involves a follicular scan where you visit the doctor’s office almost every day to check if you are ovulating.
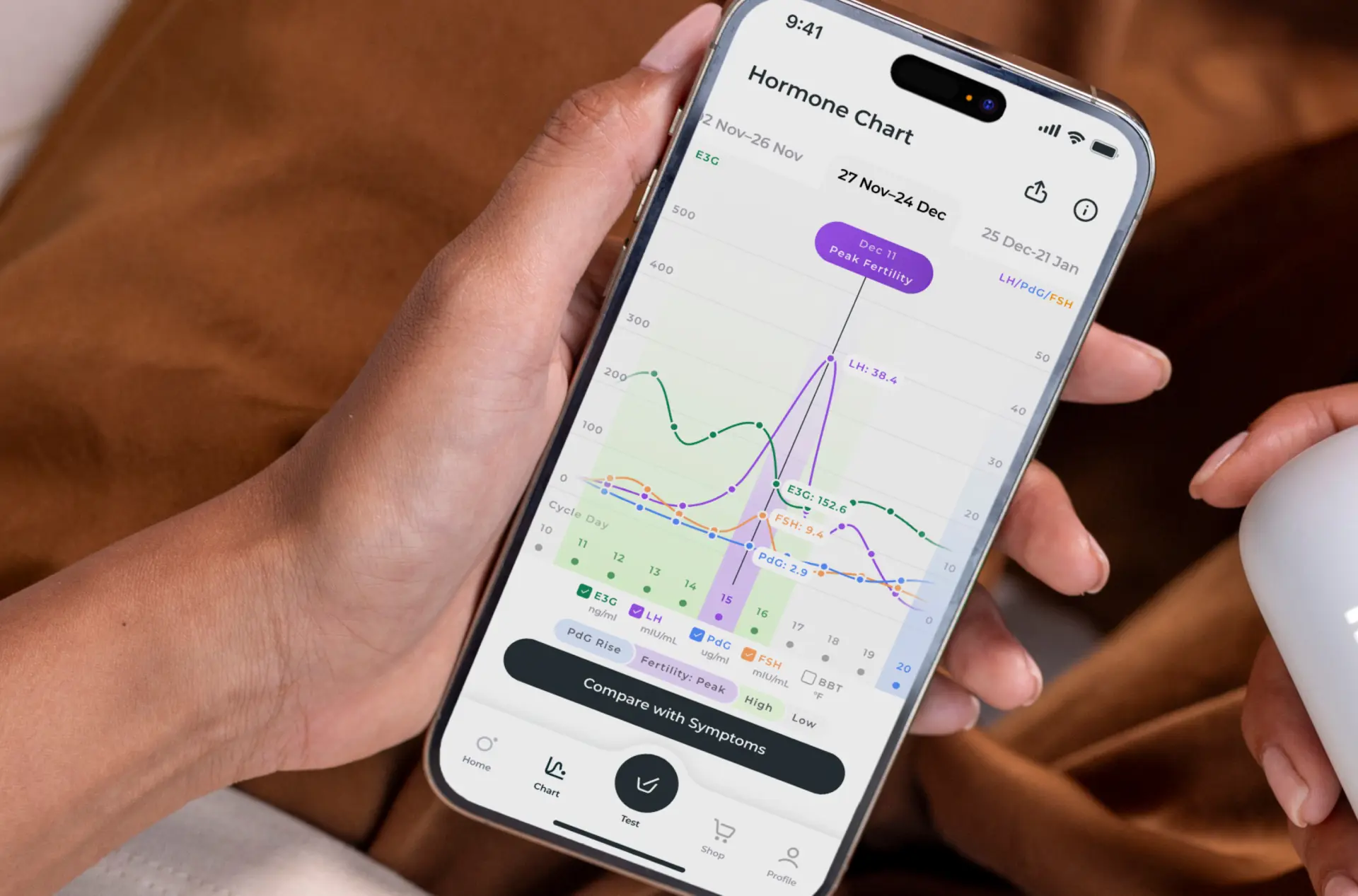
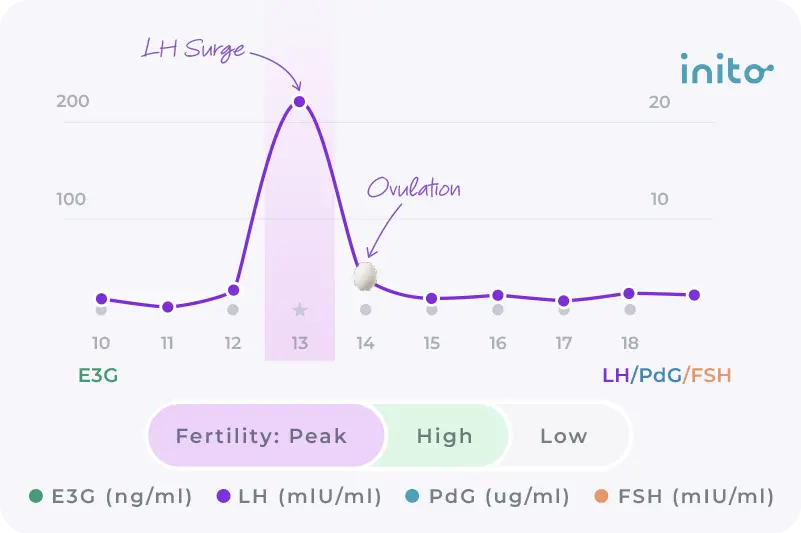
If you go the LH surge route, you can use a fertility monitor like the Inito monitor.
An advantage of the Inito monitor is that it gives you the exact values of your luteinizing hormone (LH). This allows you to track your LH more carefully so you’re less likely to miss your surge. One less thing to stress about!
And on top of that, the Inito monitor also tracks your estrogen and FSH levels to give you a full picture of your fertile window, as well as your PdG (urine metabolite of progesterone) levels to help you confirm that you actually ovulated.
4. Sperm preparation
Once you know your ovulation window, the next step is preparing the sperm. In “sperm washing,” a specialist will separate the healthy sperm from the seminal fluid. They’ll also take out abnormal and non-motile sperm.
This step ensures the sample used for the IUI is concentrated with the highest quality sperm. Sperm washing takes about 90 minutes, and it can significantly increase the odds of fertilization!
(FYI: this is one of the main differences between IUI and intracervical insemination. With ICI, the sperm sample is unwashed. But since it’s more affordable and can be done at home, it may be worth considering.)
Know more: How Much Sperm Does it Take to Get Pregnant?
If you use “fresh” sperm, the male partner will provide a fresh semen sample the day of the IUI procedure. Depending on the fertility clinic, this can be done on site or at home.
If you use frozen sperm, the fertility clinic will thaw and prepare the sperm in time for the procedure.
5. Insemination
Finally, we’ve arrived at the insemination part of the whole procedure!
The timing of the insemination is critical. In a natural cycle, your fertile window is about 6 days: the 4 days before ovulation, the day of, and the day after. But with IUI, that window is shortened to about 36 hours.
The insemination will be scheduled for 24-36 hours after your LH surge or hCG trigger shot. And the procedure itself is fairly simple, only taking a few minutes.
Here’s a brief rundown of what happens during the procedure:
- While lying on your back, the doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina.
- Next, they’ll insert a catheter through your cervix into your uterus.
- Then they’ll inject the washed sperm.
- After the insemination, the doctor may ask you to remain on your back for up to 10 – 15 minutes.
At this point, you’ve seen exactly how an IUI works. But an important question remains: is IUI the right fertility treatment option for you? Keep reading to find out.
Who should consider IUI as a treatment option?
As you’ve seen from the process above, to be able to undergo an IUI, a woman will need to be able to ovulate. She’ll also need at least one unblocked fallopian tube and a healthy uterus. But let’s get even more specific about when an intrauterine insemination is most useful.
Here are common cases when IUI would be beneficial:
- Ovulatory issues
- Inability to conceive with ovulation-inducing fertility medications alone
Irregular menstrual cycles - Only one blocked fallopian tube
- Some instances of mild male factor infertility – these may include motility issues or a slightly low sperm count)
- Cases of sexual dysfunction like vaginismus or ejaculation issues
- Certain cases of unexplained infertility
- Lesbian couples
Single woman parents - Asexuality
On the other hand, IUI would not be helpful in these cases:
- Two blocked fallopian tubes
- A history of implantation issues or uterine abnormalities
- Severe male factor infertility
- When genetic testing or embryo freezing is desired
If any of the above scenarios reflect your unique situation, there’s still hope for pregnancy. You’ll want to speak to your doctor about other fertility treatment options.
If you think IUI could be the right next step though, keep reading to learn about IUI pregnancy rates.
What is the success rate of IUI?
Not surprisingly, the success rate for IUI depends on many factors. These include age, the specific fertility diagnosis, sperm health, and how many cycles are attempted.
In the chart below, you can see how IUI success rates vary based on the mother’s age:
Age (in years) | IUI success rate (%) |
30-34 | 14.5 |
35-39 | 12.6 |
40-44 | 10.0 |
45 or older | 8.9 |
As you can see, as age increases, the success rate of IUI decreases. But keep in mind that these statistics are only meant to give you a general idea of what’s possible with IUI. And age is just one of the factors.
Your situation is unique. So consult your doctor or fertility specialist to determine the best action plan for you.
If you do move forward with IUI, it’s a good idea to know about the side effects up front. Learn these next.
What are the side effects of IUI?
Thankfully, there aren’t too many side effects with IUI! Here’s a glimpse at the minor side effects you may notice:
- Temporary pelvic pain or minor cramping during the insemination
- Mild spotting after the insemination
Also, if you take any medications before the IUI, you could experience extra symptoms. Some of these include hot flashes, poor sleep, bloating, and pain at the injection site. Talk to your doctor about what to expect for the specific drug(s) used as part of your treatment plan.
Besides knowing what side effects to expect, you’re also likely wondering: What is the average cost of using IUI? We’ll break down the financial considerations in the next section!
What is the cost of IUI?
The exact cost of IUI depends on (drum roll, please) your specific circumstances.
The following factors all play a role in the overall amount you’ll have to pay:
- The fertility clinic you use
- Specific medications used (if any)
- Blood work involved
- Any potential follow-up costs (like post-IUI fertility clinic visits)
- Number of IUI cycles you may need
- What your insurance plan covers
Looking for a ballpark number? Per cycle, IUI costs range from a few hundred dollars to $2,000.
Before making a final decision about IUI, let’s take a final look at all the advantages and disadvantages.
What are the pros and cons of IUI?
Here’s the TLDR of using IUI as part of your fertility plan!
What are the advantages of IUI? | What are the disadvantages of IUI? |
Less costly than other ART methods like IVF and ICSI | Compared to IVF, the success rates are lower |
Not very invasive overall | Some side effects are possible (especially if medications are used) |
One cycle of IUI is less time-intensive than one cycle of IVF | If you experience several failed rounds of IUI, it could be more time-consuming than one successful round of IVF |
It’s a good first treatment option for individuals and couples with mild fertility challenges | The window for getting pregnant with IUI is only 36 hours vs. 6 days for a natural cycle |
Donor sperm can be used | Doesn’t allow for donor eggs, genetic testing, or embryo freezing |
Takeaways
- Intrauterine insemination (aka IUI) is a form of assisted reproductive technology. It involves inseminating prepared sperm into the woman’s uterus.
- The main steps of IUI include consultation/testing, ovulation induction, ovulation, sperm washing, and the actual insemination.
- IUI is a good fit for single women, lesbian couples, and those with mild fertility struggles. It’s also a good fit for those who need to use a sperm donor.
- Compared to IVF, IUI is less invasive and less expensive. At the same time, the success rates aren’t as high.
- If you’re wondering if IUI is a viable treatment option for you, have a chat with your healthcare provider.

FAQs
IUI only involves sperm washing and artificial insemination. With IUI, the woman will need to ovulate and the inseminated sperm must still fertilize the egg on its own. Meanwhile, IVF involves an egg retrieval (which eliminates ovulation) and an embryo transfer. In IVF, the process of fertilization happens in a lab.
The IUI procedure is not usually described as “painful.” Although, some temporary discomfort is possible during and soon after the procedure. If you use any ovulation-induction meds, you may experience additional side effects. For example, you may have some mild pain when injecting the hCG trigger shot.
Neither option is “better” than the other. They each have their pros and cons. That’s why it truly depends on your medical history and fertility goals.
Know more: IUI vs. IVF: Which fertility treatment is better for you?
Know more: IUI vs. IVF: Which fertility treatment is better for you?
A lot of factors play into the success rate for IUI. But according to one study, you have about a 10-15% chance of pregnancy in any given IUI cycle.
The success rate of intrauterine insemination (IUI) depends on your unique circumstances. But if you have a successful IUI cycle, you can expect to test positive for pregnancy about 14 days after the insemination. If you used the hCG trigger shot though, be sure to ask your doctor about when to test. This is because residual hCG from the injection could remain in your system for up to two weeks.
Was this article helpful?
- Success Rate of Inseminations Dependent on Maternal Age? – Thieme
- ART Success Rates | CDC
- Ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination in infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A comparison of drugs – European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Biology
- Assessment of multiple intrauterine gestations from ovarian stimulation (AMIGOS) trial: baseline characteristics – Fertility and Sterility
- Effect of maternal and paternal age on pregnancy and miscarriage rates after intrauterine insemination
- SART: The Difference Between IUI and IVF