Content table
If you’ve been trying to get pregnant for a while, you may find yourself looking for signs of implantation. But what exactly is implantation? What happens when it occurs and what does it feel like?
And finally, what can you do to improve the chance of successful implantation?
This article will focus on everything you need to know about this important process.
Takeaways
- Implantation is the process of a fertilized egg attaching to the lining of the uterus and is the start of a pregnancy.
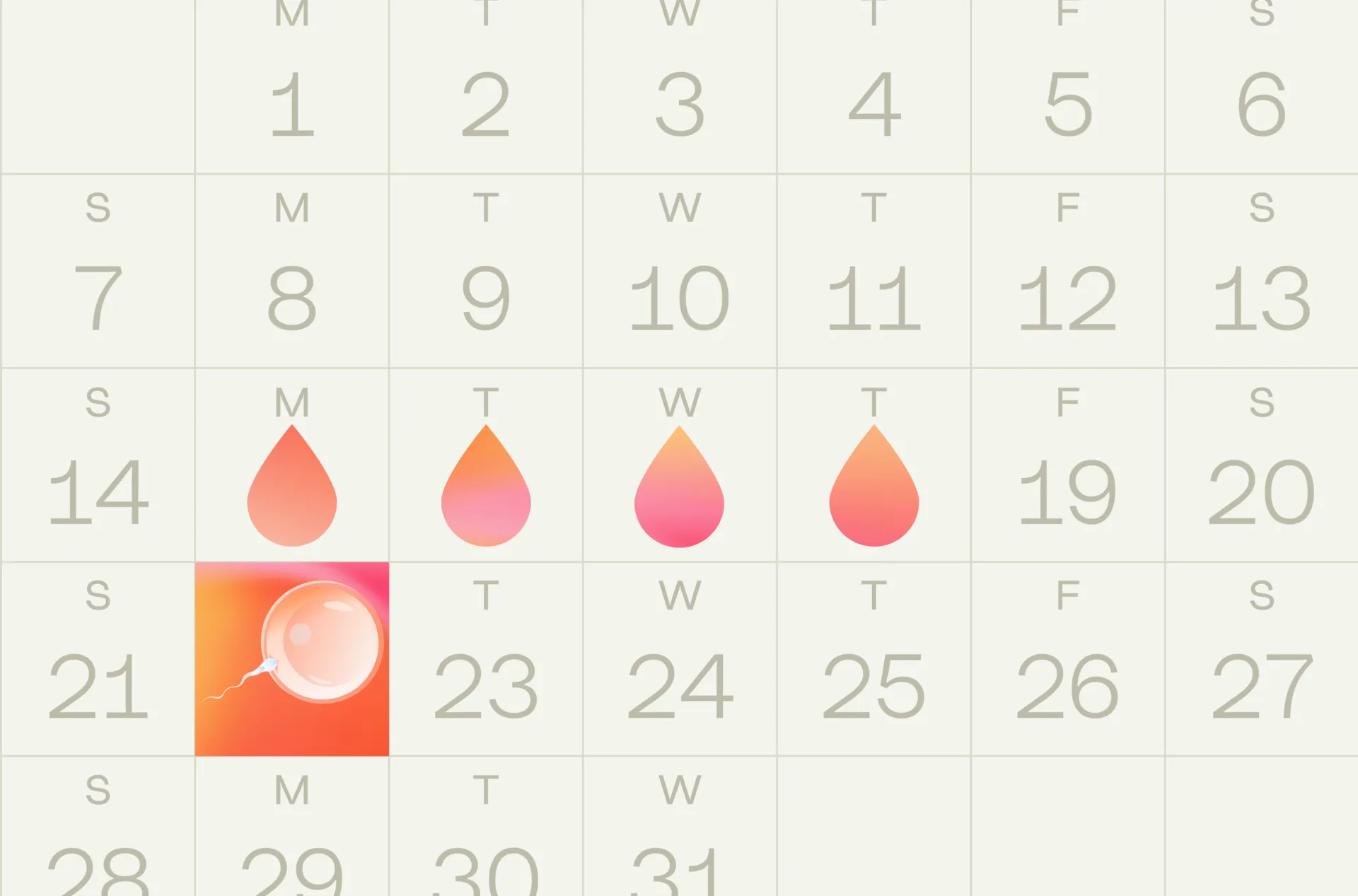
- Days 8 to 10 post ovulation are the most common days for implantation.
- Late implantation may be associated with an increased risk of miscarriage.
- Right after implantation, the embryo causes a rise in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone.
- Tracking progesterone levels at home can provide valuable information to help you get pregnant.
- Implantation can cause spotting, cramping, fatigue, bloating, and breast tenderness in some women.
What is implantation?
Before implantation can occur, ovulation and fertilization must happen first.
Ovulation, or the release of an egg from the ovary, occurs about two weeks before your period. The egg then rests in a part of the fallopian tube, known as the ampullary-isthmic junction.
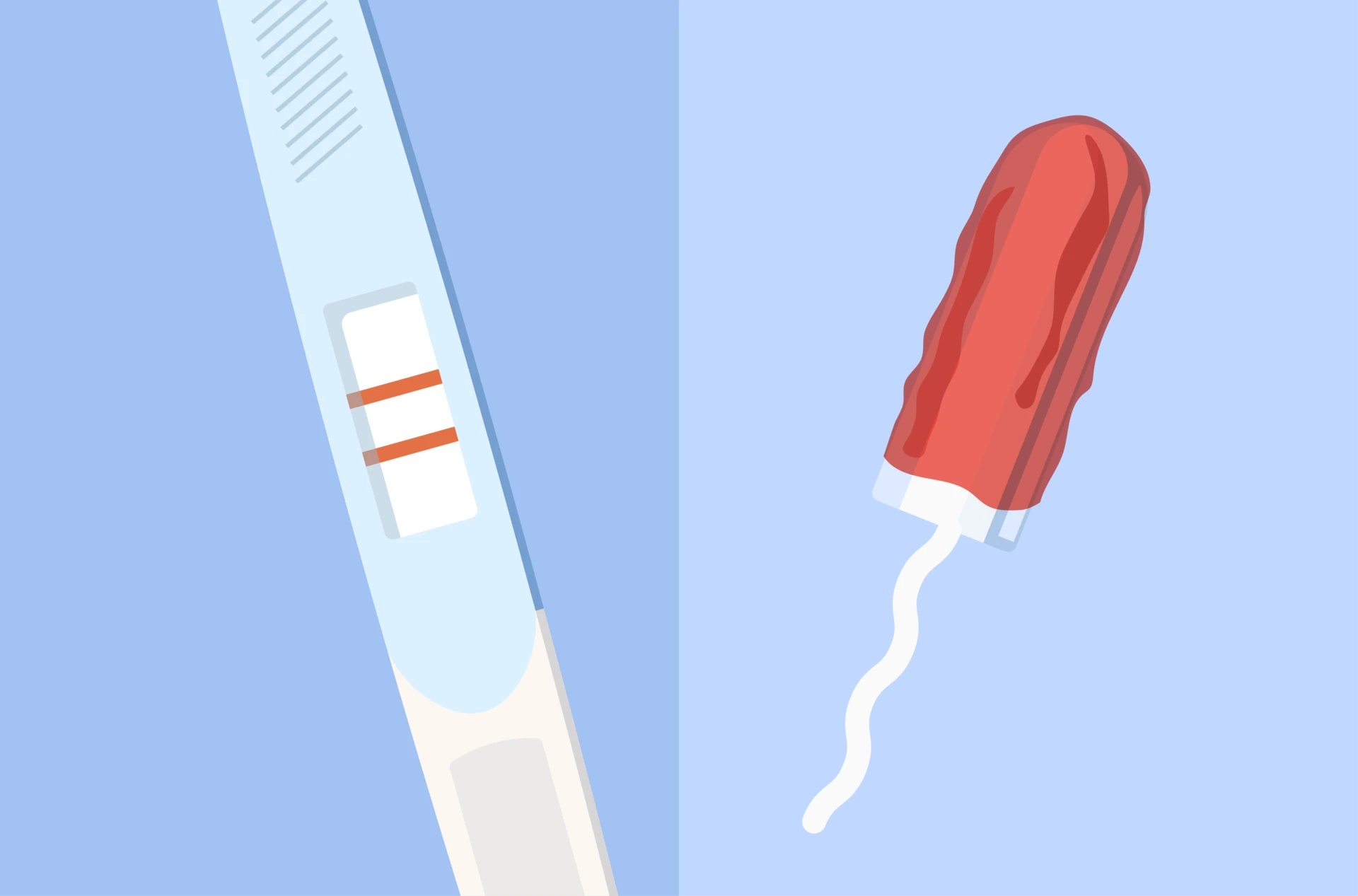
If you have unprotected sex around the time of ovulation, the egg and sperm can join together in a process known as fertilization.
This fertilized egg begins to divide in half over and over again. During this time, it begins the long journey down the rest of the fallopian tube and into the uterus. This is where implantation occurs.
Implantation is the process of a fertilized egg attaching to the lining of the uterus. This is important because it allows the growing embryo to get nutrients from the mother’s uterus so it can grow and develop.
If the fertilized egg does not implant into the uterus lining, you are not pregnant.
When does implantation occur?
Implantation can occur anytime between 6 DPO and 12 DPO (Days After Ovulation). However, it appears that days 8 to 10 are the most common.
If implantation happens 10 days after ovulation, it could mean that hormones and other factors may not be right for the pregnancy to continue.
Researchers studied the link between late implantation and the risk of miscarriage. They found that there is a higher risk of miscarriage with each day of late implantation.
Here’s a table showing the increasing percentage of miscarriage risk due to late implantation:
Implantation Day | Risk of miscarriage |
8 or 9 days after ovulation | 13% |
26% | |
11 days after ovulation | 52% |
11 + days ovulation | 82% |
How will I know if implantation has occurred?
Successful implantation depends on having a high progesterone to support the new pregnancy. Once implantation occurs, your progesterone levels start rising. The newly formed placenta also starts producing hCG.
Low or declining progesterone levels after ovulation can mean a short luteal phase. Studies show that low values of progesterone post ovulation can reduce the chances of successful implantation.
Inito can help you track your progesterone levels through its PdG (urine metabolite of progesterone) test strip. If you find your progesterone rising, you can predict a successful implantation.
What are the symptoms of implantation?
It’s different for everyone!
Some women don’t feel or notice anything out of the ordinary, while others do get some symptoms. It gets trickier because many of the symptoms of implantation are just like those of PMS. This can leave many women obsessively looking up their symptoms to figure out what is going on.
Unfortunately, it’s hard to know for sure until you either take a pregnancy test or get a full-flow period. This is because high progesterone levels happen with both PMS and implantation.
If you wish to know what happens after implantation, you need to know the symptoms of implantation. However, know that having or not having symptoms of implantation does not mean that you are or aren’t pregnant.
Possible symptoms of implantation include:
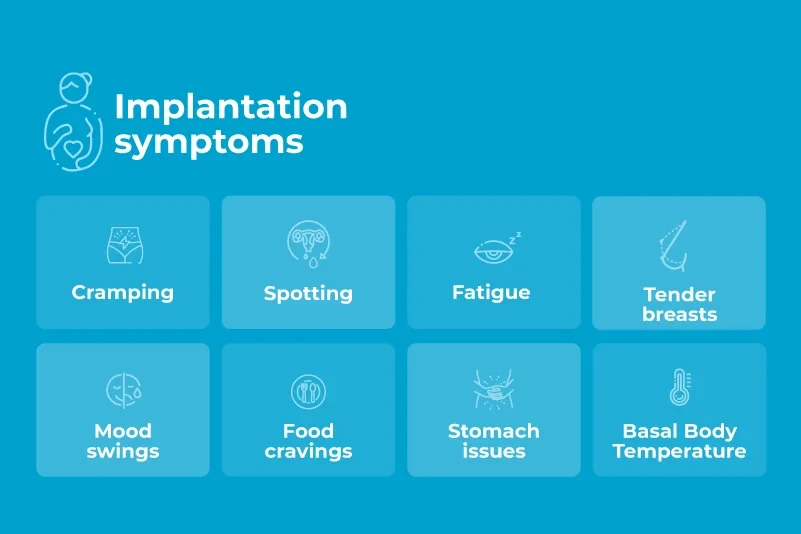
Cramping
Implantation cramping is usually felt in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or even lower back. It tends to be more in the middle of the body instead of on one side, like ovulation.
Implantation cramps are usually described as:
- Mild
- Dull
- Light twinges
- Tingling
- Pulling
- Aching
These sensations may stick around, or sometimes they come and go, but they only tend to last for a couple of days.
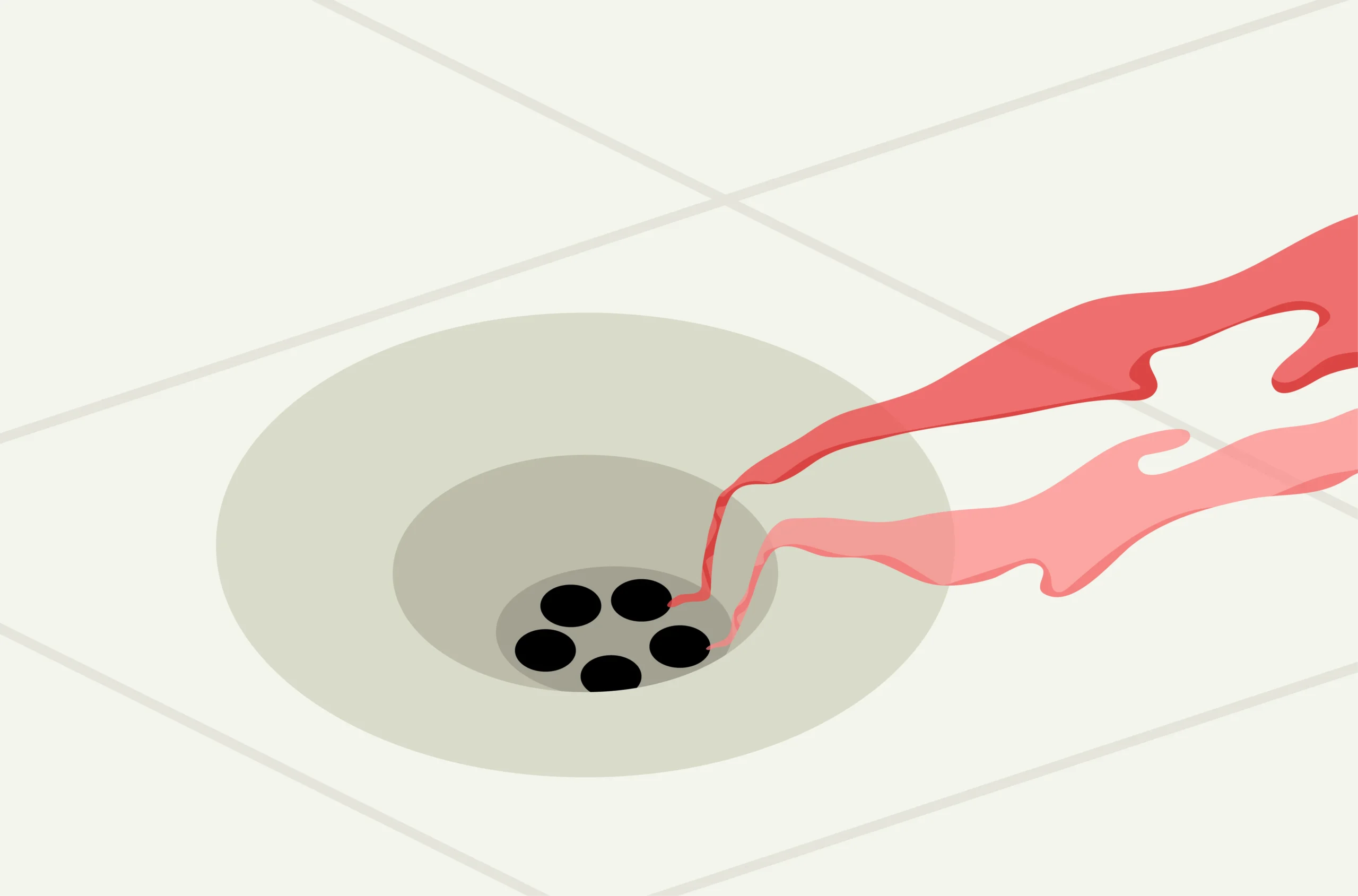
Spotting
During implantation, the fertilized egg ruptures small blood vessels in the lining. This can cause some women to experience implantation bleeding or spotting. While different for everyone, implantation bleeding typically occurs 7 to 10 days after ovulation. It is usually very light and only lasts a day or two.
Learn more: The Difference Between Implantation Bleeding and Periods
Fatigue
Fatigue is normal with high progesterone levels. This is also why you may feel more tired during the third or fourth week of your menstrual cycle (right before your period) and why exhaustion is so common in early pregnancy.
Tender breasts
Breast tenderness and sensitivity are common in the days leading up to a missed period and early pregnancy. You may also notice that your breasts appear larger; this is also due to high progesterone levels.
Mood swings
Ever cry at a really sad commercial right before your period? Yes? Thanks to rising progesterone levels. You may find yourself feeling particularly teary and emotional after implantation.
Food craving
Are you experiencing a sudden craving for pickles and ice cream? Turns out this old wives’ tale may not be such a cliché after all. High progesterone levels can not only cause food cravings but food aversions as well.
Stomach issues
In addition to making you feel sluggish and tired, progesterone can slow your stomach and intestines way down, causing constipation and bloating.
Drop in body temperature
If you test your Basal Body Temperature, you may notice the ‘Implantation Dip’—where your body temperature drops for about a day after implantation occurs.
This can also happen before getting a period. However, if implantation has occurred, your temperature will go back up. If the decrease is because you are about to get a period, the temperature will stay low.
How can I improve the chances of successful implantation?
Up to 50% of fertilized eggs may not implant and are lost during a woman’s period. If you’re trying to get pregnant, you may wonder what you can do to ensure that implantation is successful.
Well, there’s good news and bad news.
First, the good news. Embryos are quite resilient and there’s not much that you can do to affect implantation.
However, that’s also the bad news because there’s not much you can do to guarantee a successful implantation.
The best advice is to keep doing whatever you can to stay healthy. Here are a few tips:
Exercise
It is important to maintain your current level of activity. If you weren’t a marathon runner before trying to get pregnant, don’t try to be one now. Likewise, if you usually take long walks or run, it’s probably safe to continue. You may want to check in with your doctor to be on the safe side.
Prenatal vitamins
You should start taking a prenatal vitamin a few months before trying to get pregnant. Make sure that it has at least 400-800 mcg of Folic Acid to reduce the risk of a neural tube defect.
Avoid potential toxins
This includes alcohol, drugs, and cigarettes (or other nicotine products). Additionally, taking certain medications might not be great during pregnancy. Talk to your doctor if you take any medications or supplements, including over-the-counter products. You want to make sure that they are safe for conception and pregnancy.
Diet
Focus on eating a well-balanced diet that is high in nutrients and low in excess fat, sugar and calories.
Maintain a healthy weight
Being underweight or overweight can make it more difficult to conceive. The ideal BMI for getting pregnant is 18.5 to 24.9. If you’re over this range, it might take longer for you to get pregnant. Further, it might be a high-risk pregnancy. So, check your weight weekly and shed the extra pounds before conceiving.
Stress less
Stress can impact both your fertility and pregnancy. Make sure to do what you can to reduce stress and take more time for yourself. This is the time to get a massage, meet with friends, or pick up that book you’ve been waiting to read.
Please check in with your doctor if you have any concerns or questions.
Does implantation mean that you are pregnant?
Yes!
Medically speaking, implantation is the start of a pregnancy. Depending on the pregnancy test you use, you should get a positive result. Don’t forget to call your doctor and start prenatal care. Congratulations!
Was this article helpful?
Conception: How it works. Retrieved from https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/conception-how-it-works
Time of Implantation of the Conceptus and Loss of Pregnancy. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199906103402304
A Review of Mechanisms of Implantation. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5769129/#:~:text=Implantation%20consists%20of%20three%20stages,epithelial%20basement%20membrane%20and%20invade
Stages of the Development of the Fetus. Retrieved from https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/normal-pregnancy/stages-of-development-of-the-fetus